
Two resistors RL and RB connected in the circuit to limit the maximum amount of current through the transistor.
So, it is necessary to give a voltage source in reverse bias more than 0.7 V.

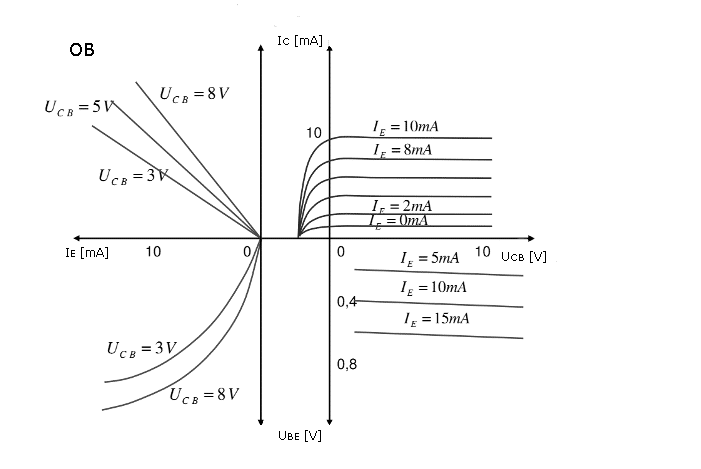
If the Base voltage is not more negative than the Emitter voltage, the current cannot flow through the device. The small amount of base current controls the flow of a large amount of current through emitter to collector provided that the Base voltage is more negative than the Emitter voltage. Like any bipolar junction transistor, the emitter-base junction is forward biased and the collector-base junction is reverse biased. This is shown in the figure below.įor p-n-p transistors, current enters into the transistor through the emitter terminal. The two p-type semiconductors act as emitter and collector respectively while the n-type semiconductor acts as a base. In PNP BJT, the n-type semiconductor is sandwiched between the two p-type semiconductors. IE = IB + IC PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) There are two types of bipolar junction transistors:īy KCL, the emitter current is the addition of base current and collector current. The direction of the arrow always points from the positive P-type region to the negative N-type region for both transistor types, exactly the same as for the standard diode symbol. The construction and circuit symbols for both the NPN and PNP bipolar transistor are given below with the arrow in the circuit symbol always showing the direction of “conventional current flow” between the base terminal and its emitter terminal. The principle of operation of the two transistors types NPN and PNP, is exactly the same the only difference being in their biasing and the polarity of the power supply for each type. This creates current between the collector and emitter, controlled by the base-emitter current.īipolar Transistors are current regulating devices that control the amount of current flowing through them from the Emitter to the Collector terminals in proportion to the amount of biasing voltage applied to their base terminal, thus acting like a current-controlled switch. The base region, between the junctions is typically very narrow. Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) are formed from two p–n junctions, three terminals device – the base, the collector, and the emitter. The fusion of these two diodes produces a three layer, two junction, three terminal devices forming the basis of a Bipolar Transistor, or BJT.
In this article, let us learn more about the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT). The word Transistor is a combination of the words Transfer and Res istor used to describe their mode of operation way back in their early days of development. The transistor’s ability to change between these two states enables it to have two basic functions: “switching” or “amplification”. Transistor are three terminal active device made from different semiconductor materials that can act as either an insulator or a conductor by the application of a small signal voltage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
